The best online experience is only possible when the different components of your internet set-up are optimised to work together. We recommend checking whether your devices, your router and any connecting cables are compatible, so you can get the most out of your nbn plan.
The right place for your router
To get the most out of the speeds offered by your nbn powered plan, you’ll need to look at the placement of your router. Obstacles like brick walls and appliances, or even the layout of your home, can impact your signal strength. You may want to even look at your in-home cabling for a faster and more reliable connection.
Your Wi-Fi router generation
Just like mobile networks have different generations (like 4G and 5G), so too does your Wi-Fi router. Each time a new generation is released, it makes way for faster speeds, and the potential for an enhanced experience.
An older router might only support slower Wi-Fi speeds, meaning it won’t be able to reach the higher speeds available on some nbn powered plans.
We recommend considering a router that supports Wi-Fi 6 (or 6E or 7). For example, for a 500Mbps plan, Wi-Fi 6 is the minimum generation recommended. Generally, the higher the number, the more advanced and the faster the data connection.

Is your router ready for the demands of tomorrow
Looking for fast and reliable speed with a wired connection? Consider a Wi-Fi router with ports that can support speeds up to 1Gbps# or higher to turbocharge your online experience.
Tip: If you’re on an nbn speed plan close to 1Gbps^, ask your provider or tech retailer about a Wi-Fi router that supports high-speed Gigabit Ethernet ports (also known as Gigabit WAN and LAN ports). These ports support speeds that could help you enjoy the full potential of your plan.
#Your router may be capable of speeds above 1Gbps, nbn's Ultrafast plan will always be less than 1Gbps due to network and equipment limitations.
^Regardless of the retail service purchased, the actual speeds delivered will be less than 1Gbps due to equipment and network limitations. An end customer’s experience, including the speeds actually achieved over the nbn network, depends on some factors outside nbn’s control (like equipment quality, software, and how a retail service provider designs its network) and the nbn technology used for the connection.

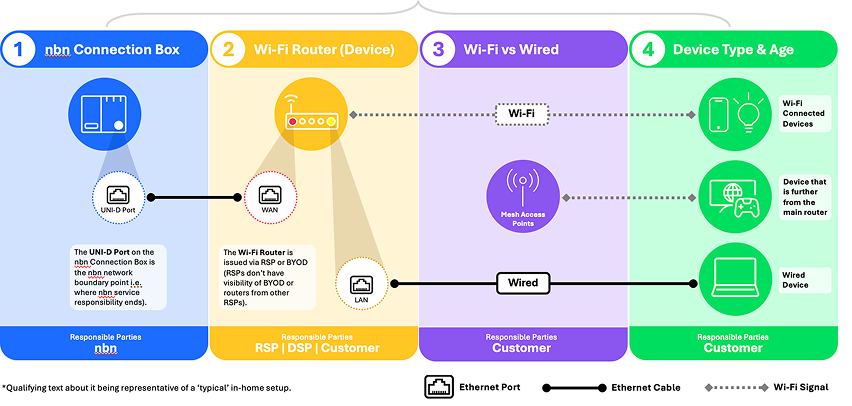
Understanding WAN and LAN
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a type of network that covers large geographical areas, such as the internet. A WAN port on your router connects your premises to this network via the nbn connection box, providing internet access to your home or business.
A Local Area Network (LAN) is your “local network", which typically starts at your router and includes your connected devices.
Your router has ports that allow you to connect to these networks, and which provide internet access to your devices:
- The WAN port is used to connect your Wi-Fi router to your nbn connection box
- The LAN port is used to connect your devices to your Wi-Fi router
The ports on your router come with various capabilities that support different speeds. Devices connected via Ethernet cable will be limited the speed of the router port, even if the device and cable support higher speeds.

Mesh coverage: when a single router isn’t enough
Larger or multi-storey properties can experience slower speeds or drop-outs when using only one Wi-Fi router. You may want to consider adding a Wi-Fi mesh network to your internet set-up.
A Wi-Fi mesh network connects multiple devices called nodes (also known as ‘access points’ or ‘satellite nodes’) to your Wi-Fi router, spreading the Wi-Fi signal further throughout your property to give you more coverage where you need it.
This enables you to get around things like thick walls, plus it covers larger spaces, so you don’t have to compromise on speed over distance. Speak to your preferred internet provider or electronic retailer to help you make an informed decision.
Advanced tip: For the optimal Wi-Fi mesh network experience, consider linking each of the access points directly to your Wi-Fi router, or mesh base station, using a wired connection like an Ethernet cable. A wired connection means you’re not purely relying on the Wi-Fi signal from your router and between access nodes, setting up your home or business with faster and more reliable internet coverage.

Mesh vs Extenders
Wi-Fi extenders, available for over 20 years, rebroadcast Wi-Fi signals around your property to expand your network coverage but often create separate networks (SSIDs), causing your devices to switch between them, creating dropouts and a disrupted experience.
In contrast, a Wi-Fi mesh network is a newer technology that forms a single, more streamlined network, so your devices can switch smoothly between nodes avoiding dropouts in the connection as you move around your home or business.
Source:
(1) Fiber Development Index Analysis – 2023 by OMDIA (page 12) – Statistic refers to households that are connected via fixed broadband.

Understanding your nbn connection box
The nbn connection box is what connects your home or business to the internet.

Wired vs Wireless - which is right for you?
To create a great online experience, you can utilise a wired connection, Wi-Fi, or a combination of both. Wi-Fi offers the freedom to move around, while fixed cabling can support data hungry devices.
More information and assistance
Would you like to learn more? Check out our list of frequently asked questions.
